
Introduction
Success of a business concern is dependent upon the ability of leadership to exist in any type of organisation. Whenever and in whatever situation if someone tries to influence the behaviour of another individual or a group, there in leadership.
In an organisation, wherever an individual has subordinates, he may act as a leader. The efforts of subordinates (followers) are to be channelised in the right direction. As lenders, they are not only the responsible for directing their followers but also responsible for the attainment of goals of the organisation. It is believed that leaders are born and not made. At the same time, a few people also believe that leaders are not born but made. But generally, leaders are born and also made.
Definition
Koontz and O’Donnell said, “Leadership is generally defined as influence, the art of process of influencing people so that they will strive willingly towards the achievement of group goals.”
Allen, “Leader is one who guides and directs other people. He must give effective direction and purpose.”
According to the Encyclopedia of Social Sciences, “Leadership refers to the relation between an individual and a group around some common interest and behaving in a manner directed or determined by him (the leader).”
George R. Terry says, “Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for mutual objectives.”
In the words of Peter F. Drucker, “Leadership is the lifting of man’s visions to higher rights, the raising of man’s performance to higher standards, the building of man’s personality beyond its normal limitations.”
Robert C. Appleby defines, “Leadership is a means of direction, is the ability of the management to induce subordinate to work towards group ideals with confidence and keenness.”
Alford and Beatty Opines, “Leadership is the ability to secure desirable actions from a group or followers voluntarily without the use of coercion.”
Ordway Tead asserts, Leadership is that combination of qualities by the possession of which one is able to get something done by others, chiefly because through his influence, they become willing to do so.”
Haimann Theo fact that, “Leadership can be defined as the process by which an executive imaginately directs, guides and influences the work of others in choosing and attaining specific goals by mediating between the individual and the organisations in such a manner that both will obtain maximum satisfaction.”
Chester I. Barnard holds, “It (leadership) refers to the quality of the behaviour of the individual whereby they guide people on their activities in organised efforts.” R.T. Livingston believes, “Leadership is the ability to awaken in others the desire to follow a common objective.”
Need & Importance of Leadership
1. Perfect organisation structure: An organisation structure cannot provide for all kinds of relationships. That is why, informal relationships are made to exist within the ог framework or formal organisation structure. But the organisation structure is complete perfect with the help of effective leadership.
2. Directing group activities: The personal conduct and behaviour of a leader can direct others to achieve organisational goals. The main responsibility of a leader is to get the work done effectively by the followers. The followers cannot work hard and effectively without leadership. A leader alone can consolidate the efforts and direct them towards the goal.
3. Technological, economic and social changes: There is frequent change in technology, economic and social structure in the present computer world. So, the organisation should change its operation and style. This is possible only with the help of effective leadership. If the changes do not take place, the organisation cannot survive.
4. Better utilisation of manpower: A leader treats with equal importance, plans, policies and programmes of an organisation. The plans, policies and programmes do not work themselves. There is a need for a leader. The leader implements the plans, policies an programmes to utilise the available manpower effectively and get highest production with minimum human cost.
5. Avoiding imbalances: An organisation grows in size and complexity with the imbalances. Complexity arises due to the introduction of new functions. The reason is that the introduction of new functions resulted in increased levels of management. So, there is a problem of command, co-ordination and control. A leader can tackle these problems and maintain balances.
6. Source of motivation: Simply, the existence of leadership does not motivate the workers. The leadership style should be utilised to motivate the workers according to the situations prevailing. The achievement of goals is doubtful in the absence of leadership.
7. Reconciliation of goals: An organisation has its own goals. The employees of the organisation have their own goals. They are working mainly for achieving their goals instead of achieving organisational goals. An effective leadership can reconcile the goals of organisations and employees. It is necessary for the success of an organisation.
8. Developing good human relations: Human relations represent the relations between the leader and the followers (subordinates). An efficient leader can develop the skill of the followers and promote self-confidence apart from motivation.
Next, the leader creates opportunity to show their abilities and induces the followers to work towards the accomplishment of goals. In this way, the leader promotes the co-operative attitude of workers and maintains better relations with them.
9. Promoting the spirit of co-ordination: A dynamic leader can co-ordinate the activities of the subordinate. In an organisation, workers are working in groups, so there is a need for co-ordination among the group members. A leader promotes the spirit of coordination among the workers.
10. Fulfiling social responsibilities: Social responsibilities refer to the high standard. of living to workers, higher productivity and income to the organisation, more revenue to the government, reasonable price to consumers and fair return on investment to the investors. These could be achieved with the help of effective leadership. Only an efficient leader can get work done to fulfil social responsibilities.
Approaches or Theories of Leadership
The various approaches or theories of leadership are discussed below:
1. Traitist’s approach or theory: Trait means quality. According to this theory, leadership behaviour is influenced by certain qualities of a person (leader). In simple words, leadership behaviour is sum total of traits. Studies were conducted to identify the qualities of past and present leaders in terms of their education, experience, character, family background, etc. Another way of finding leadership quality is to enquire how the leader considers himself different from others in a particular situation.
Researchers have found out a number of qualities of leadership from their study. A successful leader has the following qualities: (i) Good personality; (ii) Tirelessness; (iii) Ability to take quick decision; (iv) Courage to face competitors; (v) Persuasion; (vi) Lesson out of experience; (vii) Intelligence; (viii) Different thinking; (ix) Reliability; (x) Physical fitness etc.
Initially, most of the persons thought that leadership qualities were inherited but later they concluded that the acquired qualities could be developed by experience and training. So, leadership qualities are not only born but also developed. This theory was mostly accepted during 1930s and 1950s.
Check here for latest case studies and research book : https://kit.co/Anurooba/case-analysis-text-books
Weakness of Trait’s Theory
Trait’s theory suffers from the following weaknesses:
1.No common equalities list: The qualities of a successful leader are listed by various thinkers. But the list of the qualities of a thinker may not tally with the list of qualities in another thinker. At the same time, no thinker has listed the qualities in order of importance. The list of qualities have confused the readers often.
2.Measurement of quality: Thinkers simply provide the list of qualities. They fail to give the scale to measure the qualities. Besides, it is very difficult to specifiy the qualities which are necessary for an effective leader.
3.No scope for future development: Trait’s theory focuses on the inborn qualities of an individual. These inborn qualities cannot be developed or acquired. But, the inborn qualities can be developed. It has been practically proved. But, trait’s theory does not give any scope for future development of inborn qualities. The reason is that the theory assumes that leaders are born but not made.
4.No consideration for situational factors: Thinkers do not take into consideration the situation which influences the leaders. The quality of the leader comes to light only when a situation arises. If there is no situation present, there will be no scope for the use of trait or quality.
5.No need of uniform traits: Different qualities are necessary for different levels of manage-ment. There is a direct contact between the leader and the followers at the lower level management. So, there is a compulsory need for technical knowledge. The policy of the management is interpreted at middle level management.
Here, better human relations are necessary between the leaders and followers. Top management people frame the policy of the organisation. They require more skills than others. So, it is concluded that the same leadership qualities are not necessary to all the management people.Next, leadership role is very limited in the case of large organisation and vice versa.
2. Behavioural approach or theory: Thinkers diverted their attention to study leaders’ behaviours instead of leaders’ qualities. The reason is that trait’s theory has many weaknesses. Behaviour Theory had popularity during 1950s. So the behaviour approach study emerged after 1950s and 1960s.
The basis of behaviour theory lies in the fact that how the management viewed the workers. Behaviour theory assumes that people are lazy and irresponsible by nature. So there is a need of an instrument to give motivation to workers. Here, leadership acts as an instrument. The manager is an instrument holder.
Therefore, the manager should be directive. F.W. Taylor finds the behaviour of workers through his scientific management approach. Elton Mayo and his associates conducted Hawthorne experiments and identified the workers’ behaviour. They came to the conclusion that human behaviour is mainly responsible for effective leadership.
Autocratic, democratic or supervisory styles are some of the leadership styles. Behaviour approach theory developed these leadership styles which produce different and conflicting results. Different and conflicting results were obtained due to changes in the behaviour of leaders and followers. Both leaders and followers change their behaviour according to the situations.
Behaviour theory concentrated on explaining the behaviour of leaders. The behaviour of the followers changed according to the changes in the behaviour of the leaders. So, what the leader does is the main concern.
3. Situationist approach or theory: Trait theory explains the characteristics required for an effective leader. But it does not specify the person who should possess particular traits to be a leader. In case of behaviour theory, it explains the leadership styles available to leaders but fails to recommend the last best leadership style. Both these theories initiated further researches and accepted that situation is also an important element. During 1970s the situation theory was developed.
The usefulness of traits and behaviours is tested in a particular situation. Some traits and behaviours are effective in a particular situation and ineffecitve in another situation. As per the situation theory, a leader is strongly affected by the situation in which he works. Situation helps the persons to develop their leadership qualities and emerge as leaders.
Here, traits or behvaiours are supporting elements to the leaders. Situation theory believes that there is an interlink between the group of workers and its leaders. Some group of workers have aspirations. They follow the leaders who one capable of realising their aspirations. Thus, it is the situation that shapes the leadership qualities.
4. Follower’s theory or acceptance Theory: According to this theory, only followers decide whether a person is a leader or not. Followers take a decision analysing the qualities of the person who helps to have their needs fulfilled. Here, there is a need for forming a group and fulfilling some needs of such a group. This theory cannot be applied without a group of followers.
Traits and behaviour are not considered as essential elements of leadership. Under this theory, if followers accept a person as their leader, he becomes a leader irrespective of his qualities and behaviour. Modern managers are of the opinion that Acceptance theory plays a significant role in managing the people at present.
In the political world also, a person who satisfied the needs of his followers will become a leader. Followers disown their leader when he fails to satisfy their needs. The needs of the group are the crucial and guiding factor in determining the leader.
5. System theory or a path-goal theory: System theory is focused on a person’s act rather than his traits or behaviour. A leader co-ordinates the efforts of his followers. The process of co-ordination is done by a person (leader). It is termed as person’s act. The process of co-ordination stimulates the people to achieve the goal in a particular situation.
System theory considers all the variables. The term variable includes the leader, followers, situation, leadership traits, environment goals and group’s nature, characteristics and needs, role behaviour of the leader and co-ordination efforts of the leader. So this theory is considered as modern theory of leadership.
Check here for latest case studies and research book : https://kit.co/Anurooba/case-analysis-text-books
Functions of a Leader

The functions of a business leader are briefly explained below:
1. Taking initiative: A leader has to take all initiatives to lead the business activities. He should not except others to induce him to take initiative. He himself should come in the field and take all steps to achieve pre-determined targets.
2. Representation: A leader is a representative of an organisation. The leader represents the purpose of organisation to workers and outsiders.
3. Guide: The leader has the primary duty of guiding others. Proper direction should be given by a leader. If he does not do so, the organisation will not succeed. The leader should issue instructions and orders whenever needed. These instructions and orders should be properly communicated.
4. Encouraging others: The leader is the captain of a team. The leader must win the confidence of his colleagues before winning in a competition. The leader cannot succeed without teamwork. Encouragement is necessary to build up teamwork.
5. Arbitrator and Mediator: The leader can settle the disputes arising among the workers. Besides, he can create a smooth relationship among the workers. He performs these duties in a friendly manner. Generally, people accept friendly advice. Sometimes, the leader can act as a friend.
6. Planner: The type of activities or type of work is to be decided by the leader. The leader can decide when a work is to be done, where it should be done and by whom it should be done. This planning work is completed by the leader.
7. Rewards and Punishments: There is a standard for some set of work. Some workers perform their work within a standard time and properly. The leader can give rewards to those who have completed the work as per the standard. The leader can punish the worker who does not complete the work as per the requirements of job.
8. Integration: Each individual does a part of a whole work. They perform the work according to their specialisation. Here, there is a need for integration. So the leader integrates the efforts of all workers. In this way, integration is one of the functions of the leader.
9. Communication: Communication is necessary to every organisation. Nothing will succeed without effective communication. An effective commu-nication system conveys the authority and responsibility to each individual so that he may come to know what he is to do and what not.
An individual understands his authority and responsibility from organisational policies, procedures and programmes. The leader should arrange for an effective communication system in an organisation.
10. Production: A leader is expected to show high production figures. A production oriented style is followed by the leader. He should take all necessary steps to increase production.
Qualities of Leadership
A leader should have some leadership qualities in order to provide effective leadership. According to Henry Fayol, a leader should have the qualities of:
(i) health and physical fitness,
(ii) mental vigour and energy,
(iii) courage to accept responsibility,
(iv) steady, persistent thoughtful determination,
(v) sound general education, and
(vi) management ability embracing foresight and the art of handling men.
The important qualities of a leader are discussed below:
1. Physical appearance and strength: The leader has to put in hard work physically. He should have a capacity to work for long hours than others. It proves the diligence of the leader to his followers easily.
2. Mental vigour: The leader is also strong mentally. It means that the leader is expected to withstand strain in finishing the work properly.
3. Emotional stability: The leader should not be moved by emotion or sentiment. He should analyse the problem rationally and take a decision without bias. The leader should not have short temper. Besides, he should show firmness in his decision and not show despair or indecision on his face.
4. Sense of judgement: A leader should know the human psychology. He should understand the behaviour, needs, thoughts, motives etc. of his followers. This will help him to take a strategic decision and get it recognised by his followers. Besides, he can set right his actions.
5. Goodwill: A leader should be able to understand the feelings of others. He takes decision on the basis of expectations of his followers. If he does not do so, he will not win the goodwill of his followers.
6. Motivation: A leader should know the motivation techniques and how to use them. If a person is forced to do his job under the threat of getting punishment, he will not perform his work properly. At the same time, if the same person is motivated, he will perform his job more than the expectations of his leader.
7. Communication skill: Whatever the information needed to workers, it should be passed through the leader. So, the leader should communicate the information to the workers. Now, the leader is acting as an effective speaker and writer. If the leader has communication skills, he will direct his followers effectively.
8. Guiding ability: The leader acts as a teacher to new workers. So the leader helps his followers to learn their work. He should train the workers by work and deed to complete the job effectively.
9. Sociability: An able leader can easily mingle with the workers. The workers should be encouraged to discuss their problems and difficulties with their boss. The leader should also meet the workers frequently. The leader should show his keen interest to develop the ability of workers.
10. Technical knowledge: A leader should possess a thorough knowledge of the theory and practice of his job. Besides, he should know the current developments in his job along with technical knowledge.For example, a computer department manager should know all the latest developments in computers.
These are some qualities of a leader. Besides, he should be honest, sincere and fair. Sincere, fair and honest people are mostly liked by others and their leadership is accepted by one and all.
Types of Leaders

Leadership cannot exist without followers. The characteristics of the followers play a vital role in the exercise of leadership. The behaviour of a leader is based on the maturity levels of the followers. Here, maturity level refers to job enrichness and psychological maturity (motivation) of followers.
Thus, the leader has to adopt task behaviour if he has low level maturity followers and tell them what, when, where and how the given work is to be completed. In other words, if the leader has high-level mature followers, he can adopt assigning behaviour and the entire work along with freedom to complete the work. The types of leaders are classified on the basis of behaviour of leaders. They are briefly explained below:
1. Autocratic leader: A leader is one who wants to run the organisation all by himself. He frames the objectives of the organisation and requires the followers to achieve the objectives. These objectives are expected to be achieved within the time limit fixed by him. Besides, he gives specific directions to his followers and he is regularly informed of the progress in work.
A leader thinks that his followers do not have much ability to do a job effectively. So, he avoids discussions with his followers regarding job completion. The leader does not delegate any authority to his followers. He has close supervision and control over his followers. He uses the technique of giving rewards and/or punishments to his followers.
If any follower completes his job according to the expectations of the leader, he will be rewarded. On the other hand, if any follower fails to complete his job as per the requirements, he will be penalised and the punishment may be in the form of company action or dismissal.
2. Intellectual leader: A leader wins the confidence of his followers by his intelligence. Generally, the advice of a leader is sought in big business concerns. He gives advice on the matter in which he is expert. He may be a specialist in sales, personnel management and the like. He gets results through others. He excels as a leader because he uses his superior knowledge.
3. Liberal leader: A leader is one who permits his followers to do their job howsoever they want to do. The leader has not framed any policy or procedure which the followers are expected to follow in their jobs.
The liberal leader would not exercise any influence over his followers and vice versa. Wide scope and opportunities are available for free discussion which aims at performing the job effectively. The followers should have a high degree of maturity.
High degree of maturity means the followers have both the ability and willingness to work. If the followers have low maturity, the leader cannot succeed in his position. In other words, whenever the liberal leader has low maturity followers, he is not able to make his followers understand what, how, when and where to perform.
4. Democratic leader: A leader acts according to the wishes of his followers. The leader does what his followers want. The leader frames the policy or procedure according to the opinion of the majority of his followers. He acts as a representative of his followers to management.
The leader holds his leadership because he is loyal to his followers. He is always interested in protecting the interests of his followers. The leader is a friend of his followers and he is helpful to them.
5. Institutional leader: A leader exercises his power over his followers because of his position held in the organisational hierarchy. He exercises authority with which his post is invested. The leader can control the activities of his followers in order to achieve the objectives.
The leader may or may not be an expert in his field. If he is an expert, he will have relationship behaviour with his followers. If he is not so, he has task behaviour with his followers. The followers prefer relationship behaviour to task behaviour. Whenever the leader adopts task behaviour, the followers are frustrated.
6. Inducing leader: The leader is one who influences his followers with his personality and persuades them to join him in doing a work. He loves and is loved by his followers. The followers have confidence in him and want his goodwill.
The leader gets things done by others through speaking nice words. The whole gang responds to the words of the leader.
7. Paternal leader: An individual who has become the leader in the place of his father as leader has close relationship with his followers and comes to their rescue ever so often.
Paternal leader has job maturity followers only. The reason is that the followers may be lacking only in their psychological maturity. They are not permitted to show their initiative. The leader lays certain conditions under which the followers are expected to work. So the followers are not aware of their potential fully.
8. Creative leader: The leader is one who encourages his followers to suggest new ideas, thoughts or ways. Sometimes, the leader himself puts forward new ideas. Whenever more than one new idea flows from the group, the leader will select the best one among them without personal bias. He controls his followers just like other leaders and makes them to achieve the specific goals. According to Ordway Tead, the followers adopt the big idea but not the big.
A BEST WAY TO EARN WHILE YOU STUDY, JOIN THIS APP UPLOAD PHOTOS, SAVE MONEY FROM NOW ON : https://bit.ly/3g7PxAg
Technique of Leadership
A leader can use a number of techniques to extract work from his followers. Some of the techniques are discussed below:
1. Securing co-operation: A leader should get co-operation from his followers. Unless he enlists their co-operation, he cannot succeed. There must be a willingness on the part of both parties. The leader must convince each follower to extend co-operation.
Both leaders and their followers must have interest in the growth of an enterprise. First, the leader himself extends his co-operation to his followers. The leader must treat his followers as co-workers and not as followers.
2. The use of power: Leadership goes with power. It cannot exist without power. So the leader must use his power which subsequently results in getting things done by others. At the same time, the leader should use power only to safeguard the interests of the enterprise. Some leaders expect more powers than required. It is not advisable. On the other hand, a leader can achieve the goals with the available power.
3. Co-ordination: A leader can co-ordinate the activities of his followers or commands. Definite, flexible and open orders alone co-ordinate the activities. Definite order means that an order is not oral and the terms used in definite order have unequivocal meaning. In the case of flexible order, only goals are communicated. Next, the followers achieve the goals by using the pre-determined time. A leader specifies the goals and leaves the other details to his followers in open order.
An order fulfils its purpose only when it is properly received and receiver must know the expectation of the issuer. Then only proper results will be obtained.
4. Discipline: Discipline is nothing but the adherence to rules, regulations and procedures. Discipline should be maintained to achieve the objectives. Individuals are restricted from doing things which are detrimental to the group interests. If a particular follower is violating the rules, he may be penalised. The very success of leadership and organisation depends upon the maintenance of discipline.
5. Morale: Leighton has defined morale, as the capacity of a group to pull together persistently and consistently for a common goal. “Morale is the attitude of an individual and group growing out of the conditions under which he or they complete the job effectively.”
The leader should create confidence in the minds of his followers. Here, confidence is necessary to both the leader and the followers. A leader has confidence in his followers and vice versa. Mental maturity plays an important role in creating confidence. Having confidence ensures effective performance of a job.
Characteristics of Leadership

1. There must be followers: A leadership cannot exist without followers. A leader who does not have followers, he cannot exercise his authority. Leadership exists both in formal and informal organisations.
2. Working relationship between leader and followers: It means that the leader should present himself in a place where the work is actually going on. Besides, the leader should be a dynamic person of the concerned group. If he is not so, he cannot get things done.
3. Personal quality: The character and behaviour of a man influence the works others.
4. Reciprocal relationship: Leadership kindles a reciprocal relationship between the leader and his followers. A leader can influence his followers and, in turn, the followers can influence the leader. The willingness of both the leader and the followers is responsible for the influence and no enforcement is adopted.
5. Community of interests: There must be community of interests between the leader and his followers. A leader has his own objectives. The followers have their own objectives. They are moving in different directions in the absence of community of interests. It is not advisable. It is the leader who should try to reconcile the different objectives and compromise the individual interests with organisation interests.
6. Guidance: A leader guides his followers to achieve the goals of the organisation. A leader should take steps to motivate his followers for this purpose.
7. Related to particular situation: Leadership is applicable to a particular situation at a given point of time. It varies from time to time.
8. Shared Function: Leadership is a shared function. A leader is also working along with his followers to achieve the objectives of the organisation. Besides, the leader shares his experience, ideas and views with his followers.
9. Power relationship: A leader has powers to exercise over his followers. The leader derives these powers from the organisation hierarchy, superior knowledge, experience and the like.
A BEST WAY TO EARN WHILE YOU STUDY, JOIN THIS APP UPLOAD PHOTOS, SAVE MONEY FROM NOW ON : https://bit.ly/3g7PxAg
Leadership Styles
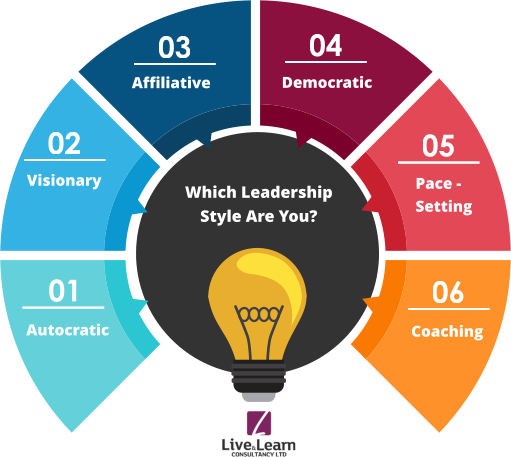
The success of a business unit depends upon the leadership styles followed by the leaders. Leadership style describes how a leader has relationship with his group. Some of the leadership styles are discussed below:
1. Positive style: A leader motivates his followers to work hard by offering them rewards. A rule is framed in such a way that a reward will be ensured to those who show high efficiency. Positive leaders promote industrial peace. For example, higher bonus (bonus linked with wages) will certainly increase efficiency of the workers. Wages are payable under piece rate system.
2. Negative style: A leader forces his followers to work hard and penalises them if the work is not upto the organisation’s standard. The penalty is given according to the performance. The penalty will be a severe one if the performance has more short comings.
For example, if the manager gives ousting order for continuous absence from duty for ten days even though the worker is absent due to unavoidable circumstances. It is a negative style.
Negative style has high human cost. But, it is necessary in some circumstances. Under negative style, everybody tries to shift his responsibility over to others. Negative style leaders act more as bosses than leaders.
3. Autocratic or authoritarian style: Under this leadership style, the leaders have full power or authority to take a decision. The leaders create a work situation under which the subordinates are expected to work. They will work no more or less than the instruction of the leader. So, the leaders have full responsibility.
The followers are not aware of organisation goals. Besides, the followers feel insecure and are afraid of the authority of the leaders. The reason is that these leaders have the desire to wield loving more powers. Sala
The leader uses his power for the interest of his group and motivate his followers. Then the productivity is increased and the followers get full satisfaction from their job. Advantages
1. This leadership style provides strong motivation to the followers.
2. Quick decision is possible. The reason is that the leader himself takes decision for the whole group.
3. Less talented followers can perform their job effectively.
4. Followers need not take any decision.
5. Decision-making, planning or organising need no initiative.
The autocratic leadership style has some disadvantages. They are given below:
Disadvantages
1. Most of the people dislike this style. The reason is that this style has a negative motivation approach.
2. Frustration, low morale and conflict develop easily under autocratic leadership. 3. New ideas or creative ideas of the followers will not have a scope to be applied and benefits of these could not be obtained under autocratic style.
4. The followers have no opportunity for development.
Suitability
Autocratic style is not suitable to all business organisations. It is suitable to those organisations in which the followers are uneducated and unskilled. The reason is that they are unable to take decisions. If the organisation follows the punishment principle, this leadership style may be suitable.
4. Democratic style: It is otherwise called as participative style. It is just opposite to autocratic style. The authority is decentralised. So, the followers are permitted to take decisions under this style. The decisions are taken wholeheartedly. The reason is that the superior has consultation with his subordinates before taking a decision.
The subordinates know the goals of the organisation, so, they offer fruitful ideas during discussion. If a leader follows this style, he can use the force to control his followers instead of using authority.
Generally, most of the leaders follow this style. At present, the worker’s participation in management is gaining popularity.
Advantages
1. Consultation gives satisfaction to the followers. Followers are consulted before taking a decision.
2. Due recognition is given to the followers. So, they show more interest in increasing the company’s productivity.
3. Followers are aware of the activities in the organisation.
4. A leader can improve his decision-making ability through consultation with his followers while taking a decision.
5. Followers get opportunity to show their ability or talent.
Disadvantages
1. Decentralisation of power is used only when consultation is made for taking a decision. Nothing more than that is done.
2. Taking a decision and the implementation of it require more time. The reason is that several members are involved in taking a decision.
3. Followers can dominate the leader.
4. A leader can easily shift the responsibility to his followers for failure in taking and implementing a decision.
5. It requires communicating skill on the part of the leader. If does not have it, unfavourable things may happen in an organisation and the organisation may be financially and status-wise ruined.
5. Free-rein style: The leaders have no authority and responsibility under this style, so the followers themselves take decisions for which they get authority. This style is employee-centred. Employees (Followers) are free to establish their own goals and chart out the course of action. The employees train themselves and they are self-motivated.
The leader acts as a laison officer between the employees and the outside world. He brings the information which is needed to the employees. The information is utilised by the employees to do their job. Here, the leader fails to motivate his followers (Employees).
Advantages
1. Morale and job satisfaction of the followers are increased to some extent.
2. The talent of the followers is properly utilised.
3. The followers get full opportunity to develop their talents.
Disadvantages
1. The leader does not care to motivate his followers.
2. The contribution of a leader is nothing.
3. The leader does not support the follower and no guidance is available to the former.
Im very pleased to find this page. I wanted to thank you for your time due to this wonderful read!! I definitely savored every bit of it and i also have you bookmarked to check out new information in your blog.